<1, 2>
(a) Core-type Furnaces- जो एक two winding transformer की तरह काम करता है। इन्हें और sub-divided किया जा सकता है (i) Direct core-type furnaces (ii) Vertical core-type furnaces and (iii) Indirect core-type furnaces.
(b) Coreless-type Furnaces — जिसमें radiation द्वारा charge में heat को
transfer करने के लिए एक inductively-heated element बनाया जाता है।
This furnace suffers from the following drawbacks :
1. इसे low-frequency supply पर चलाया जाना चाहिए जो motor-generator set या
frequency converter पर extra expenditure को पूरा करता है।
2. यह pinching effect से suffers है।
3. charge के लिए crucible odd shape का है और molten हुए charge को tapping करने के लिए very inconvenient है।
4. यह काम नहीं करता है अगर hearth में कोई molten metal नहीं है यानी जब secondary
open होता है। furnace को शुरू करने के लिए हर बार molten metal को डालना पड़ता है।
5. यह intermittent service के लिए suitable नहीं है। हालांकि, इस furnace में, melting तेजी से और साफ होता है और temperature को easily controlled किया जा सकता है।
इसके अलावा, electro-magnetic forces द्वारा charge की inherent stirring action end product की अधिक uniformity सुनिश्चित करती है।
coreless induction के कुछ लाभ इस प्रकार हैं::-
(1) वे operation में fast हैं।
(2) वे product की सबसे uniform quality का उत्पादन करते हैं।
(3) इन्हें आपस में operated किया जा सकता है।
(4) इनका संचालन smoke, dirt, dust और noises से मुक्त है।
(5) इनका उपयोग सभी industrial applications के लिए किया जा सकता है जिनमें heating और melting की आवश्यकता होती है।
(6) इनका निर्माण और operating cost कम है।
(7) इनका charging और pouring simple है।
where ρ = resistivity of the molten metal
f = supply frequency
µr = relative permeability of the charge
(2) यह vacuum या other special environs में हो सकता है जहाँ अन्य प्रकार के heating possible नहीं हैं।
(3) Heat की supply body की किसी भी depth में penetrate के लिए की जा सकती है।
Applications of Eddy-current Heating
(1) Surface Hardening:- जिस bar की surface को heat treatment द्वारा harden किया जाना है उसे working coil के भीतर रखा जाता है जो high frequency की a.c. supply से connected होती है। depth तक, जिसे surface को harden करना है, coil current की frequency के proper selection द्वारा obtained किया जा सकता है। कुछ seconds, के बाद, जब surface proper temperature पर पहुंच गई, तो a.c. supply cut off है और bar water में डूबा हुआ है।
(2) Annealing:- Normally तौर पर, annealing process में metal के scaling में long time लगता है जो undesirable है। हालांकि, eddy-current heating में, time बहुत कम होता है ताकि कोई scale formation न हो।
(3) Soldering:- Eddy-current heating सprecise high-temperature soldering के लिए economical है जहां silver, copper और उनकी alloys को solder के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है।
इसे high-frequency capacitative heating भी कहा जाता है और इसका उपयोग wood, plastics और ceramics आदि जैसे insulators को heat करने के लिए किया जाता है, जिन्हें easily और uniformly रूप से other methods से heat नहीं किया जा सकता है। dielectric heating के लिए required supply frequency 10-50 MHz के बीच है और applied voltage 20 kV तक है। dielectric heating की overall efficiency लगभग 50% है।
जब एक practical capacitor एक ac supply में connect होता है, तो यह एक current draw करता है जो voltage को एक angle φ की ओर ले जाता है, जो 90 ° से थोड़ा कम होता है या angle δ से 90 ° कम हो जाता है। इसका मतलब है कि current का एक certain component है जो voltage के साथ phase में है और इसलिए कुछ loss produce करता है जिसे dielectric loss कहा जाता है।50 Hz की normal supply frequency पर, यह loss negligibly से small है, लेकिन 50 MHz की higher frequencies पर या तो यह loss इतना बड़ा हो जाता है कि यह dielectric को heat करने के लिए sufficient है जिसमें यह होता है। heat की जाने वाली insulating material को दो conducting plates के बीच रखा जाता है ताकि एक parallel-plate capacitor बनाया जा सके जैसा कि figure (a) में दिखाया गया है।
figure (b), capacitor के equivalent circuit को show करता है और figure (c) अपने vector diagram को show करता है
Power drawn from supply = VI cos φ
Now, Ic = I =V/Xc = 2πf CV
∴ P = V(2πfCV ) cos φ = 2πfCV 2 cos φ
Now, φ = (90 – δ), cos φ = cos (90 – δ) = sin δ = tan δ = δ
where δ is very small and is expressed in radians.
P = 2πfCV 2δ watts
यह power heat में convert हो जाती है। चूंकि किसी दिए गए insulator material के लिए, C और δ constant हैं, इसलिए dielectric loss V 2f के directly proportional होता है।
इसीलिए dielectric heating में high-frequency voltage का उपयोग किया जाता है। Generally, 10-30 MHz की frequency पर लगभग 20 kV a.c. voltage का use किया जाता है।
Advantages of Dielectric Heating:-
1. चूंकि heat dielectric medium के भीतर generate होती है, इसलिए यह uniform
heating होता है।
2. increasing frequency के साथ heating fast हो जाता है।
3. यह bad conductors को heat करने की एकमात्र method है।
4. Heating is fastest in this method of heating.
5. चूँकि इस process में कोई naked flame दिखाई नहीं देती है, इसलिए plastics और wooden के products आदि जैसे inflammable articles को safely heated किया जा सकता है।
6. Heating can be stopped immediately as and when desired.
Applications of Dielectric Heating:-
चूंकि dielectric heating की cost very high है, इसलिए इसे employed किया जाता है जहां other methods possible नहीं हैं या बहुत slow हैं। dielectric heating के कुछ applications निम्नानुसार हैं:
1. multilayer plywood boards के gluing के लिए।
2. sand cores के baking के लिए जो moulding process में उपयोग किया जाता है।
3. उन्हें moulding section में भेजने से पहले plastic compound को preheating करने के लिए।
4. cigarattes बनाने के लिए glycerine के बाद tobacco को drying के लिए इसमें mixed किया जाता है।
5. automatic machines की सहायता से bakeries में biscuits और cake आदि को baking के लिए।
6. high-frequency supply के साथ cold rollers की मदद से plastic garments जैसे raincoats आदि की electronic sewing के लिए।
7. food की dehydration के लिए जो फिर air-tight container में seal कर दिया जाता है।
8. oil emulsions से moisture निकालने के लिए।
9. human body के different parts में pain से राहत के लिए diathermy में।
10. book binding purposes के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले glue के quick drying के लिए।
heating के लिए frequency का selection important है क्योंकि यह heat होने के work पर बहुत असर डालता है और इसके heating की method चाहे induction heating या dielectric heating. 50 Hz की power frequency पर चलने वाले furnaces 1 MW capacity के हो सकते हैं जबकि medium frequencies (500 Hz to 1000 Hz) पर चलने वालों की capacity 50 kW और high frequency (1 MHz to 2 MHz) पर running की capacity होती है। 200 kW से 500 kW।
1. Induction Heating:- induction heating के लिए frequency का चयन करते समय, निम्नलिखित factors प रconsider किया जाता है:
(a) surface के heat होने की thickness. Higher frequency, surface को thin करती है जो heat हो जाएगी।
(b) continuous heating का time. Long time तक heating की duration, conduction के कारण work में heat के penetration को deep.
(c) obtained होने वाला temperature. Higher temperature, required generator की capacity अधिक होती है।
2. Dielectric Heating:- dielectric heating, P = 2πfCV 2 cos φ के दौरान consumed की गई power। जैसा कि देखा गया है, P ∝ f × C × V 2 × cos φ. इसलिए, किसी भी specimen के across voltage या voltage को increase करके heat production की rate को increase किया जा सकता है, इसकी thickness limited है या potential gradient, breakdown voltage और safety आदि के consideration के कारण, 600 V से 3000 V तक के voltage का उपयोग dielectric heating के लिए किया जाता है। हीटिंग, हालांकि 20 kV या उससे अधिक voltages का भी कभी-कभी उपयोग किया जाता है। high potential को apply करके heat production की rate भी increase की जा सकती है, लेकिन यह निम्न कारणों से भी limited है:
(a) used की गई particular frequency की wavelength के लगभग एक चौथाई या उससे अधिक के equal wavelength वाले दो electrodes की surface के बीच standing waves के formation की possibility।
(b) इस तथ्य के कारण higher frequencies पर special matching circuit को employ करने की आवश्यकता है कि maximum power transfer तब होता है जब oscillator impedance load impedance के equal होती है।
(c) higher frequencies पर charge capacitance के साथ resonate tuning के लिए difficult है।
(d) higher frequencies पर, uniform voltage distribution प्राप्त करना लगभग impossible है।
(() चूंकि higher frequencies radio station service के near विचलित करती हैं, इसलिए इस purpose के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले high-frequency generator से radiations को रोकने के लिए special arrangement की जानी चाहिए।
Induction Heating
यह heating process heat होने के लिए electro-magnetic action द्वारा induced
currents का उपयोग करती है। वास्तव में, induction heating transformer के working
principle पर आधारित है। primary winding जो कि a.c. source को magnetically रूप से coupled किया जाता है जो single turn के short circuited secondary के रूप में कार्य करता है। जब एक a.c. voltage को primary पर applied किया जाता है, यह secondary में voltage induce करता है यानी charge करता है। secondary current charge को उसी तरह heat करता है जैसे कोई electric current किसी resistance से गुजरते समय होता है। यदि V charge में voltage induced है और R charge resistance है, तो heat produced = V 2 / R होता है। charge में induced current का मान निम्नलिखित पर depends करता है (i) primary current की magnitude पर (ii) transformer के turn ratio पर और (iii) magnetic coupling के co-efficient पर।
Low-frequency induction furnaces का use different metals को melting और refining के लिए किया जाता है। हालांकि, other processes जैसे case hardenning और soldering etc. के लिए, high-frequency वाले eddy-current heating को employed किया जाता है।metals के melting के लिए employed furnaces निम्नलिखित दो प्रकार की होती हैं:
(a) Core-type Furnaces- जो एक two winding transformer की तरह काम करता है। इन्हें और sub-divided किया जा सकता है (i) Direct core-type furnaces (ii) Vertical core-type furnaces and (iii) Indirect core-type furnaces.
(b) Coreless-type Furnaces — जिसमें radiation द्वारा charge में heat को
transfer करने के लिए एक inductively-heated element बनाया जाता है।
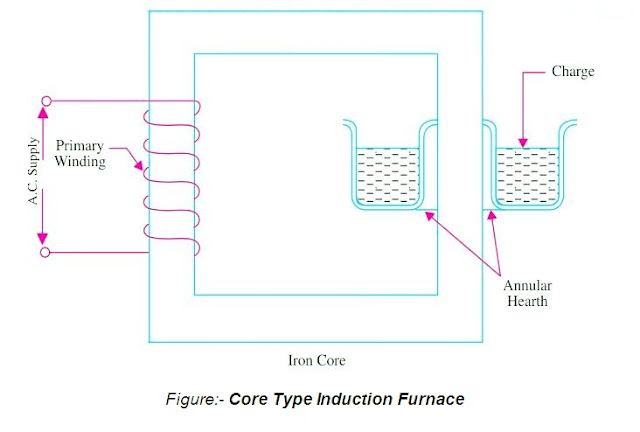
Core Type Induction Furnace:-
यह Figure में दिखाया गया है और यह essentially रूप से एक transformer है जिसमें heat किया जाने वाला charge एक single-turn short-circuited secondary बनता है और primary रूप से iron core से magnetically coupled होता है। furnace में एक circular hearth होता है जिसमें एक annular ring के रूप में पिघल जाने का प्रभार होता है। जब ring में कोई पिघला हुआ metal नहीं होता है, तो secondary open-circuited हो जाता है-secondary current को cutting करके।
इसलिए, furnace को start करने के लिए, annular hearth में molted metal डालना पड़ता है।चूंकि, primary और secondary के बीच magnetic coupling बहुत poor होता है, इसके परिणामस्वरूप high leakage और low power factor होता है। increased हुई leakage reactance, के effect को कम करने के लिए, 10 Hz के order की low primary frequency का उपयोग किया जाता है।
यदि transformer secondary current density 500 A / cm2 से अधिक हो जाती है, तो alternating magnetic ield के साथ secondary current की परस्पर क्रिया के कारण, molten metal इस हद तक सिकुड़ जाता है कि secondary circuit interrupted हो जाता है।यह effect को “pinch effect” के रूप में जाना जाता है।
This furnace suffers from the following drawbacks :
1. इसे low-frequency supply पर चलाया जाना चाहिए जो motor-generator set या
frequency converter पर extra expenditure को पूरा करता है।
2. यह pinching effect से suffers है।
3. charge के लिए crucible odd shape का है और molten हुए charge को tapping करने के लिए very inconvenient है।
4. यह काम नहीं करता है अगर hearth में कोई molten metal नहीं है यानी जब secondary
open होता है। furnace को शुरू करने के लिए हर बार molten metal को डालना पड़ता है।
5. यह intermittent service के लिए suitable नहीं है। हालांकि, इस furnace में, melting तेजी से और साफ होता है और temperature को easily controlled किया जा सकता है।
इसके अलावा, electro-magnetic forces द्वारा charge की inherent stirring action end product की अधिक uniformity सुनिश्चित करती है।
Vertical Core-Type Induction Furnace:-
इसे Ajax-Wyatt furnace के रूप में भी जाना जाता है और above discussed की गई core-type furnace पर improvement को represents करता है। जैसा कि figure में दिखाया गया है, इसमें charge के लिए vertical channel (instead of a horizontal one) है, ताकि use किया गया crucible भी vertical हो जो metallurgical point से सुविधाजनक हो। इस furnace में, magnetic coupling comparatively रूप से बेहतर होता है और power factor high होता है। इसलिए, इसे normal frequency supply से operate किया जा सकता है।
molten metal का circulation convection currents द्वारा Vee portion को round रूप में रखा जाता है जैसा कि figure में दिखाया गया है। चूंकि Vee channel narrow है, यहां तक कि small quantity में charge भी secondary circuit को closed रखने के लिए पर्याप्त है। हालाँकि, secondary circuit की continuity बनाए रखने के लिए Vee channel को पूरी तरह से charge रखा जाना चाहिए। यह तथ्य इस furnace को continuous operation के लिए उपयुक्त बनाता है। pinch-effect के कारण secondary circuit के rupture की tendency crucible में charge के weight द्वारा counteracted होती है।
 |
| Figure:- Vertical Core-Type Induction Furnace |
furnace के inner lining के लिए material की choice उपयोग किए गए charge के प्रकार पर depends करती है। Clay lining का उपयोग yellow brass के लिए किया जाता है। red brass और bronze के लिए, magnetia और alumina या corundum के एक alloy का उपयोग किया जाता है। furnace का top एक insulated cover के साथ cover किया गया है जिसे charging के लिए remove किया जा सकता है। furnace को पिघला हुआ metal बाहर निकालने के लिए उपयुक्त hydraulic arrangement द्वारा झुकाया जा सकता है। यह furnace व्यापक रूप से brass और अन्य non-ferrous metals के melting और refining के लिए उपयोग की जाती है। जैसा कि पहले कहा गया था, यह continuous operation के लिए suitable है।
यह एक p.f. 0.8-0.85 के normal supply frequency के साथ, इसकी efficiency लगभग 75% है और इसका standard size 60-300 kW, सभी single-phase से भिन्न होता है।
Indirect Core-Type Induction Furnace:-
इस furnace में, एक suitable element को induction द्वारा heat किया जाता है, जो बदले में radiation द्वारा charge को heat में transfers करता है। जहां तक charge की बात है, तो conditions एक resistance oven के समान हैं। जैसा कि figure में दिखाया गया है, secondary में एक metal container होता है जो furnace की walls को proper बनाता है। primary winding magnetically रूप से एक iron core द्वारा इस secondary के लिए coupled है।
 |
| Figure:- Indirect Core-Type Induction Furnace |
जब primary winding जुड़ा हुआ है a.c. supply से , तो secondary current metal container में transformer action द्वारा induced होता है जो container को heat करता है। metal container इस heat को charge में transfer करता है। इस furnace का एक विशेष लाभ यह है कि इसके temperature को external equipment के उपयोग के बिना automatically controlled किया जा सकता है।
oven chamber के अंदर स्थित magnetic circuit के भाग AB में एक special alloy होती है जो एक particular temperature पर अपने magnetic properties को खो देता है, लेकिन वापस उसी temperature पर cool होने पर उन्हें पुन: प्राप्त कर लेता है। जैसे ही chamber critical temperature को प्राप्त करता है, magnetic circuit की reluctance कई गुना बढ़ जाती है जिससे heat supply बंद हो जाती है। bar AB detachable है और इसे अलग-अलग critical temperature वाले other bars द्वारा replaced किया जा सकता है।
Coreless Induction Furnace:-
जैसा कि figure में दिखाया गया है, furnace के three main parts हैं (i) primary coil (ii) एक ceramic crucible युक्त charge होता है जो secondary बनाता है और (iii) frame का निर्माण करता है जिसमें supports और tilting mechanism शामिल होता है। इस furnace की विशिष्ट विशेषता यह है कि इसमें कोई heavy iron core नहीं है जिसके परिणामस्वरूप magnetic flux के लिए कोई continuous path नहीं है।
crucible और coil निर्माण में अपेक्षाकृत हल्के हैं और pouring के लिए आसानी से tilt किया जा सकता है। charge को crucible में put किया जाता है और primary winding high-frequency a.c. supply से connect होता है। primary द्वारा flux produce में eddy-currents को set करता है और इसे melting point तक heat करता है। charge शुरू में molten state में नहीं होना चाहिए जैसा कि core-type furnaces में required था। eddy- currents ने electromotive forces को भी स्थापित किया जो stirring action produce करते हैं जो metal की uniforms quality प्राप्त करने के लिए आवश्यक है।
 |
| Figure:- Coreless Induction Furnace |
चूंकि flux का density कम है (magntic core की absence के कारण) high frequency supply का उपयोग करना पड़ता है क्योंकि eddy-current loss We ∝ B2f 2 है। हालांकि, यह high frequency skin effect के कारण primary winding के resistance को बढ़ाती है , जिससे primary Cu losses increase होती हैं। इसलिए, primary winding copper wire से नहीं बने होते हैं, लेकिन hollow copper tubes से बने होते हैं, जो उनके circulating water से cool होते हैं। चूंकि primary और secondary windings के बीच magnetic coupling low है, furnace p.f. 0.1 और 0.3 के बीच स्थित है। इसलिए, static capacitors को अपने p.f को बेहतर बनाने के लिए furnace के साथ parallel रूप से use किया जाता है।
इन furnaces का use commonly steel production के लिए और इन elements के various alloys के साथ-साथ non-ferrous metals जैसे कि brass, bronze, copper और aluminum आदि के melting के लिए किया जाता है। इन furnaces के special application में vacuum melting, एक controlled atmosphere में melting और precision casting के लिए vacuum melting शामिल है जहां high frequency induction heating का उपयोग किया जाता है। यह electronic industry और अन्य industrial activities जैसे soldering, brazing hardening और annealing और sterilizing surgical instruments आदि का व्यापक उपयोग करता है।
coreless induction के कुछ लाभ इस प्रकार हैं::-
(1) वे operation में fast हैं।
(2) वे product की सबसे uniform quality का उत्पादन करते हैं।
(3) इन्हें आपस में operated किया जा सकता है।
(4) इनका संचालन smoke, dirt, dust और noises से मुक्त है।
(5) इनका उपयोग सभी industrial applications के लिए किया जा सकता है जिनमें heating और melting की आवश्यकता होती है।
(6) इनका निर्माण और operating cost कम है।
(7) इनका charging और pouring simple है।
High Frequency Eddy-current Heating:-
eddy-currents द्वारा article को heat करने के लिए, इसे high frequency a.c. current-carrying coil के inside placed किया जाता है (figure)। coil द्वारा produced alternating magnetic field article में eddy-currents को set करता है, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप heat हो जाता है। ऐसे coil को heater coil या work coil के रूप में जाना जाता है और heat होने वाली material को charge या load के रूप में जाना जाता है। Primarily रूप से, यह eddy-current loss है जो heat के production के लिए responsible है हालांकि hysteresis loss भी non-magnetic materials के case में कुछ हद तक contributes देता है। eddy-current loss We ∝ B2f 2 . इसलिए, इस loss को flux density B और supply frequency ƒ को controll करके controlled किया जा सकता है। यह loss material की surface पर सबसे बड़ा है लेकिन decrease हो जाता है क्योंकि हम deep से inside होते हैं। material की depth तक, जिसमें eddy current loss penetrate है, द्वारा दिया जाता है।
where ρ = resistivity of the molten metal
f = supply frequency
µr = relative permeability of the charge
Advantages of Eddy-current Heating
(1) heat का negligible wastage होता है क्योंकि body में heat produce होने के लिए heated होती है।(2) यह vacuum या other special environs में हो सकता है जहाँ अन्य प्रकार के heating possible नहीं हैं।
(3) Heat की supply body की किसी भी depth में penetrate के लिए की जा सकती है।
Applications of Eddy-current Heating
(1) Surface Hardening:- जिस bar की surface को heat treatment द्वारा harden किया जाना है उसे working coil के भीतर रखा जाता है जो high frequency की a.c. supply से connected होती है। depth तक, जिसे surface को harden करना है, coil current की frequency के proper selection द्वारा obtained किया जा सकता है। कुछ seconds, के बाद, जब surface proper temperature पर पहुंच गई, तो a.c. supply cut off है और bar water में डूबा हुआ है।
(2) Annealing:- Normally तौर पर, annealing process में metal के scaling में long time लगता है जो undesirable है। हालांकि, eddy-current heating में, time बहुत कम होता है ताकि कोई scale formation न हो।
(3) Soldering:- Eddy-current heating सprecise high-temperature soldering के लिए economical है जहां silver, copper और उनकी alloys को solder के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है।
Dielectric Heating:-
इसे high-frequency capacitative heating भी कहा जाता है और इसका उपयोग wood, plastics और ceramics आदि जैसे insulators को heat करने के लिए किया जाता है, जिन्हें easily और uniformly रूप से other methods से heat नहीं किया जा सकता है। dielectric heating के लिए required supply frequency 10-50 MHz के बीच है और applied voltage 20 kV तक है। dielectric heating की overall efficiency लगभग 50% है।
Dielectric Loss:-
जब एक practical capacitor एक ac supply में connect होता है, तो यह एक current draw करता है जो voltage को एक angle φ की ओर ले जाता है, जो 90 ° से थोड़ा कम होता है या angle δ से 90 ° कम हो जाता है। इसका मतलब है कि current का एक certain component है जो voltage के साथ phase में है और इसलिए कुछ loss produce करता है जिसे dielectric loss कहा जाता है।50 Hz की normal supply frequency पर, यह loss negligibly से small है, लेकिन 50 MHz की higher frequencies पर या तो यह loss इतना बड़ा हो जाता है कि यह dielectric को heat करने के लिए sufficient है जिसमें यह होता है। heat की जाने वाली insulating material को दो conducting plates के बीच रखा जाता है ताकि एक parallel-plate capacitor बनाया जा सके जैसा कि figure (a) में दिखाया गया है।
 |
| Figure:- Dielectric Loss |
figure (b), capacitor के equivalent circuit को show करता है और figure (c) अपने vector diagram को show करता है
Power drawn from supply = VI cos φ
Now, Ic = I =V/Xc = 2πf CV
∴ P = V(2πfCV ) cos φ = 2πfCV 2 cos φ
Now, φ = (90 – δ), cos φ = cos (90 – δ) = sin δ = tan δ = δ
where δ is very small and is expressed in radians.
P = 2πfCV 2δ watts
यह power heat में convert हो जाती है। चूंकि किसी दिए गए insulator material के लिए, C और δ constant हैं, इसलिए dielectric loss V 2f के directly proportional होता है।
इसीलिए dielectric heating में high-frequency voltage का उपयोग किया जाता है। Generally, 10-30 MHz की frequency पर लगभग 20 kV a.c. voltage का use किया जाता है।
Advantages of Dielectric Heating:-
1. चूंकि heat dielectric medium के भीतर generate होती है, इसलिए यह uniform
heating होता है।
2. increasing frequency के साथ heating fast हो जाता है।
3. यह bad conductors को heat करने की एकमात्र method है।
4. Heating is fastest in this method of heating.
5. चूँकि इस process में कोई naked flame दिखाई नहीं देती है, इसलिए plastics और wooden के products आदि जैसे inflammable articles को safely heated किया जा सकता है।
6. Heating can be stopped immediately as and when desired.
Applications of Dielectric Heating:-
चूंकि dielectric heating की cost very high है, इसलिए इसे employed किया जाता है जहां other methods possible नहीं हैं या बहुत slow हैं। dielectric heating के कुछ applications निम्नानुसार हैं:
1. multilayer plywood boards के gluing के लिए।
2. sand cores के baking के लिए जो moulding process में उपयोग किया जाता है।
3. उन्हें moulding section में भेजने से पहले plastic compound को preheating करने के लिए।
4. cigarattes बनाने के लिए glycerine के बाद tobacco को drying के लिए इसमें mixed किया जाता है।
5. automatic machines की सहायता से bakeries में biscuits और cake आदि को baking के लिए।
6. high-frequency supply के साथ cold rollers की मदद से plastic garments जैसे raincoats आदि की electronic sewing के लिए।
7. food की dehydration के लिए जो फिर air-tight container में seal कर दिया जाता है।
8. oil emulsions से moisture निकालने के लिए।
9. human body के different parts में pain से राहत के लिए diathermy में।
10. book binding purposes के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले glue के quick drying के लिए।
Choice of Frequency:-
heating के लिए frequency का selection important है क्योंकि यह heat होने के work पर बहुत असर डालता है और इसके heating की method चाहे induction heating या dielectric heating. 50 Hz की power frequency पर चलने वाले furnaces 1 MW capacity के हो सकते हैं जबकि medium frequencies (500 Hz to 1000 Hz) पर चलने वालों की capacity 50 kW और high frequency (1 MHz to 2 MHz) पर running की capacity होती है। 200 kW से 500 kW।
1. Induction Heating:- induction heating के लिए frequency का चयन करते समय, निम्नलिखित factors प रconsider किया जाता है:
(a) surface के heat होने की thickness. Higher frequency, surface को thin करती है जो heat हो जाएगी।
(b) continuous heating का time. Long time तक heating की duration, conduction के कारण work में heat के penetration को deep.
(c) obtained होने वाला temperature. Higher temperature, required generator की capacity अधिक होती है।
2. Dielectric Heating:- dielectric heating, P = 2πfCV 2 cos φ के दौरान consumed की गई power। जैसा कि देखा गया है, P ∝ f × C × V 2 × cos φ. इसलिए, किसी भी specimen के across voltage या voltage को increase करके heat production की rate को increase किया जा सकता है, इसकी thickness limited है या potential gradient, breakdown voltage और safety आदि के consideration के कारण, 600 V से 3000 V तक के voltage का उपयोग dielectric heating के लिए किया जाता है। हीटिंग, हालांकि 20 kV या उससे अधिक voltages का भी कभी-कभी उपयोग किया जाता है। high potential को apply करके heat production की rate भी increase की जा सकती है, लेकिन यह निम्न कारणों से भी limited है:
(a) used की गई particular frequency की wavelength के लगभग एक चौथाई या उससे अधिक के equal wavelength वाले दो electrodes की surface के बीच standing waves के formation की possibility।
(b) इस तथ्य के कारण higher frequencies पर special matching circuit को employ करने की आवश्यकता है कि maximum power transfer तब होता है जब oscillator impedance load impedance के equal होती है।
(c) higher frequencies पर charge capacitance के साथ resonate tuning के लिए difficult है।
(d) higher frequencies पर, uniform voltage distribution प्राप्त करना लगभग impossible है।
(() चूंकि higher frequencies radio station service के near विचलित करती हैं, इसलिए इस purpose के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले high-frequency generator से radiations को रोकने के लिए special arrangement की जानी चाहिए।







0 Comments