<1, 2>

Electric heating
Electric heating का व्यापक रूप से domestic और industrial अनुप्रयोगों के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है। Domestic applications में शामिल हैं (i) room heaters (ii) immersion heaters for water heating (iii) hot plates for cooking (iv) electric kettles (v) electric irons (vi) pop-corn plants (vii) electric ovens for bakeries and (viii) electric toasters आदि।
Electric heating के industrial applications में शामिल हैं (i) metals का melting (ii) metals का heat treatment जैसे annealing, tempering, soldering और brazing आदि (iii) glass का moulding (iv) insulators का baking (v) copper के wires की enamelling आदि।
Advantages of Electric Heating:-
(i) Cleanliness:- चूंकि electric heating में न तो dust और न ही ash का उत्पादन होता है, इसलिए यह cleaning की minimum cost की आवश्यकता होती है। इसके अलावा heat होने वाली material दूषित नहीं होती है।
(ii) No Pollution:- चूँकि electric heating में कोई भी flue gases नहीं बनती है, इसलिए उनके बाहर निकलने का कोई provision नहीं किया गया है।
(iii) Economical:- Electric heating economical है क्योंकि electric furnaces अपनी
initial cost के साथ-साथ maintenance cost में भी सस्ती हैं क्योंकि उन्हें installation या coal और wood के storage के लिए big space की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है। इसके अलावा, कोई
chimney बनाने या extra heat installation provide करने की आवश्यकता नहीं है।
(iv) Easy of Control:- Manual या automatic devices की मदद से एक electric furnace के temperature को control करना आसान है। Temperature को ± 5°C के भीतर controlled किया जा सकता है जो किसी अन्य प्रकार के heating में संभव नहीं है।
(v) Special Heating Requirement:- Special heating requirements जैसे कि किसी material का एकसमान heating or उसके किसी अन्य भाग को प्रभावित किए बिना कार्य का एक विशेष भाग गर्म करना या बिना oxidation वाले heating को केवल electric heating द्वारा पूरा किया जा सकता है।
(vi) Higher Efficiency:- Electrically रूप से produced heat chimney और other
उत्पादों के through waste नहीं जाती है। consequently, produced heat का अधिकांश
उपयोग material को heat करने के लिए किया जाता है। इसलिए, other types के heating के compare में electric heating की higher efficiency होती है।
(vii) Better Working Conditions:- चूंकि electric heating में कोई irritating करने वाला noises पैदा करता है और साथ ही radiation के नुकसान कम होते हैं, इसके परिणामस्वरूप low ambient का temperature होता है। इसलिए, electric furnaces के साथ काम करना सुविधाजनक और cool है।
(viii) Heating of Bad Conductors:- Heat और electricity के खराब conductors जैसे
wood, plastic और bakery items को समान रूप से और उपयुक्त रूप से dielectric heating process के साथ heat किया जा सकता है।
(ix) Safety:- Electric heating काफी सुरक्षित है क्योंकि यह controlled signals पर quickly responds देता है।
(x) Lower Attention and Maintenance Cost:- Electric heating equipment को generally तौर पर बहुत attention और supervision की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है और उनकी maintenance cost लगभग negligible होती है। इसलिए, heating के अन्य रूपों की compare में labour charges भी small होता है।
Different Methods of Heat Transfer
1. Conduction 2. Convection 3. Radiation
1. Conduction:- heat transfer की इस mode में, body का one molecule heat हो जाता है और कुछ heat को adjacent molecule और इतने पर transfers करता है। body के दो ends के heat होने के बीच एक temperature gradient होती है।
cross-section A sq.m. की एक solid material पर consider करें और thickness x metre जैसा कि figure में दिखाया गया है। यदि T1 और T2 °K में slab के दो sides का
temperature है, तो time t seconds opposite faces के बीच heat conducted दिया गया है:

जहां K material की thermal conductivity है
2. Convection:- इस process में, hot और cold air currents के flow से heat को
transferred किया जाता है। यह process immersion heater या buildings के heating
द्वारा water के heating में applied होती है। convection process द्वारा body body absorbed heat की मात्रा मुख्य रूप से heating element के temperature पर
surroundings के ऊपर और heater की surface के size पर depends करती है। यह कुछ हद तक heater की position पर भी depends करता है। उच्छृंखल ताप की मात्रा द्वारा दी जाती है
The amount of heat dissipated is given by
H = a (T1 – T2), जहां a और b constant है और T1 और T2 क्रमशः temperatures की surface का heating हैं और ° K में द्रव हैं।
electric की furnaces में convection द्वारा transferred heat negligible है।
3. Radiation:- यह intervening medium को affect किए बिना एक straight line में एक hot body से एक cold body में heat का transfer है। heat emission की दर Stefan’s law के अनुसार दी गई है
इस method में जिस material (या charge) को heat किया जाना है उसे एक resistance के रूप में माना जाता है और current को इसके through से passed किया जाता है। charge powder, small solid pieces या liquid के रूप में हो सकता है। two electrodes charge में insert किये जाते हैं और या तो a.c. या तो d.c. supply (in Figure).
Obviously, d.c या single-phase a.c. supply के case में two electrodes की आवश्यकता होती है लेकिन 3-phase supply के case में three electrodes होते है। जब charge small pieces के रूप में होता है, तो direct short circuit से बचने के लिए charge के surface पर high resistivity material का एक powder छिड़का जाता है। जब इसमें से current passes होता है तो heat produce होती है। heating की इस method में high efficiency होती है क्योंकि heat
charge में ही produced होती है।
heating की इस method में electric current को एक resistance element से गुजारा जाता है जिसे एक electric oven में रखा जाता है। produced heat को heating element के लिए I2R loss के proportional होता है। produced heat को radiation या convection द्वारा या दोनों के combination से charge तक पहुंचाया जाता है। कभी-कभी, resistance एक cylinder में रखा जाता है जो jacket में लगाए गए charge से घिरा होता है जैसा कि figure में दिखाया गया है। यह arrangement uniform temperature provides करती है। इसके अलावा, automatic temperature control भी provide किया जा सकता है।
(3) Low Temperature Coefficient of Resistance:- यदि material में resistance का coefficient कम होता है, तो इसके temperature की normal range पर इसके resistance में केवल small variations होंगे। इसलिए, cold होने पर heating element द्वारा drawn किया गया current (i.e., at start) heat होने पर practically रूप से समान होगा।
(4) High Oxidising Temperature:- long life को सुनिश्चित करने के लिए heating element का oxidisation temperature अधिक होना चाहिए।
(5) Positive Temperature Coefficient of Resistance:- यदि heating element के resistance का temperature coefficient negative है, तो इसका resistance temperature में वृद्धि के साथ decrease हो जाता है और यह अधिक current draw करेंगा जो अधिक watt और हीट produce करेगा अधिक heat के साथ, resistance कम हो जाएगा जिसके परिणामस्वरूप operation की instability होगी।
(6) Ductile:- चूंकि heating elements की material में सुविधाजनक shapes और sizes होना आवश्यक है, इसलिए इसमें high ductility और flexibility होना चाहिए।
surroundings के ऊपर और heater की surface के size पर depends करती है। यह कुछ हद तक heater की position पर भी depends करता है। उच्छृंखल ताप की मात्रा द्वारा दी जाती है
The amount of heat dissipated is given by
H = a (T1 – T2), जहां a और b constant है और T1 और T2 क्रमशः temperatures की surface का heating हैं और ° K में द्रव हैं।
electric की furnaces में convection द्वारा transferred heat negligible है।
3. Radiation:- यह intervening medium को affect किए बिना एक straight line में एक hot body से एक cold body में heat का transfer है। heat emission की दर Stefan’s law के अनुसार दी गई है
जहां K radiating efficiency है और e को heating element की emissivity के रूप में जाना जाता है।
यदि d heating wire का diameter है और इसकी total length l है, तो इसकी surface का area जहाँ से heat radiated है = π x d x l . यदि H heating surface के per m2
radiated power है, तो total power heat = π x d x l . के रूप में radiate होती है।
यदि P heating element के लिए electrical power input है, तो P = πdl x H .
Methods of Electric Heating:-
Basically, heat एक resistance के through से current के circulation के कारण उत्पन्न होती है। potential difference के application के कारण current directly circulate हो सकता है या यह induced eddy currents के कारण हो सकता है। इसी तरह, magnetic materials में, heat create के लिए hysteresis losses का उपयोग किया जाता है। dielectric heating में, substance को heat करने के लिए molecular friction को नियोजित किया जाता है। electrode और heat होने वाली material के बीच established arc को heat का source बनाया जा सकता है। body को heat करने के लिए high energy particles द्वारा material की
surface पर बमबारी की जा सकती है।
general industrial और domestic purposes के लिए heat produce करने के different methods को नीचे classified किया गया है:
Resistance Heating:-
यह I2R इफेक्ट पर based है। जब current को resistance element I2R के through गुजारा जाता है तो loss होता है जो heat produces करता है।resistance heating के two methods है
(a) Direct Resistance Heating:-
इस method में जिस material (या charge) को heat किया जाना है उसे एक resistance के रूप में माना जाता है और current को इसके through से passed किया जाता है। charge powder, small solid pieces या liquid के रूप में हो सकता है। two electrodes charge में insert किये जाते हैं और या तो a.c. या तो d.c. supply (in Figure).
Obviously, d.c या single-phase a.c. supply के case में two electrodes की आवश्यकता होती है लेकिन 3-phase supply के case में three electrodes होते है। जब charge small pieces के रूप में होता है, तो direct short circuit से बचने के लिए charge के surface पर high resistivity material का एक powder छिड़का जाता है। जब इसमें से current passes होता है तो heat produce होती है। heating की इस method में high efficiency होती है क्योंकि heat
charge में ही produced होती है।
(b) Indirect Resistance Heating:-
heating की इस method में electric current को एक resistance element से गुजारा जाता है जिसे एक electric oven में रखा जाता है। produced heat को heating element के लिए I2R loss के proportional होता है। produced heat को radiation या convection द्वारा या दोनों के combination से charge तक पहुंचाया जाता है। कभी-कभी, resistance एक cylinder में रखा जाता है जो jacket में लगाए गए charge से घिरा होता है जैसा कि figure में दिखाया गया है। यह arrangement uniform temperature provides करती है। इसके अलावा, automatic temperature control भी provide किया जा सकता है।
Requirement of a Good Heating Element
(1) High Specific Resistance:- जब wire की material का specific resistance high होता है, केवल एक particular resistance (और इसलिए गर्मी) के लिए इसकी short length की आवश्यकता होगी या wire की same length और currrent के लिए, heat का उत्पादन किया जाता है अधिक हो जाएगा।
(2) High Melting Temperature:- यदि heating element के पिघलने का तापमान अधिक है, तो higher operating temperatures प्राप्त करना संभव होता है।
(2) High Melting Temperature:- यदि heating element के पिघलने का तापमान अधिक है, तो higher operating temperatures प्राप्त करना संभव होता है।
(3) Low Temperature Coefficient of Resistance:- यदि material में resistance का coefficient कम होता है, तो इसके temperature की normal range पर इसके resistance में केवल small variations होंगे। इसलिए, cold होने पर heating element द्वारा drawn किया गया current (i.e., at start) heat होने पर practically रूप से समान होगा।
(4) High Oxidising Temperature:- long life को सुनिश्चित करने के लिए heating element का oxidisation temperature अधिक होना चाहिए।
(5) Positive Temperature Coefficient of Resistance:- यदि heating element के resistance का temperature coefficient negative है, तो इसका resistance temperature में वृद्धि के साथ decrease हो जाता है और यह अधिक current draw करेंगा जो अधिक watt और हीट produce करेगा अधिक heat के साथ, resistance कम हो जाएगा जिसके परिणामस्वरूप operation की instability होगी।
(6) Ductile:- चूंकि heating elements की material में सुविधाजनक shapes और sizes होना आवश्यक है, इसलिए इसमें high ductility और flexibility होना चाहिए।
(7) Mechanical Strength:- heating element की material को अपने स्वयं के high mechanical strength चाहिए। आमतौर पर, अलग-अलग operating temperatures प्राप्त करने के लिए विभिन्न प्रकार के alloys धातुओं का उपयोग किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, constant का maximum work कर रहे temperature (45% Ni, 55% Cu) 400°C है , जो कि nichrome (50%, Ni 20% Cr) is 1150°C का है , Kantha (70% Fe, 25% Cr, 5% Al) 1200° C है और silicon carbide 1450°C है
Arc Furnaces
यदि एक sufficiently high voltage को एक air-gap में applied किया जाता है, तो air ionized हो जाती है और एक continuous spark या arc के रूप में conducting करना शुरू कर देती है जिससे intense heat produce होती है। जब electrodes carbon/graphite से बने होते हैं, तो प्राप्त temperature 3000°C-3500°C की range में होता है। arc से striking के लिए required high voltage एक variable ac supply से प्राप्त step-up transformer का उपयोग करके प्राप्त किया जा सकता है जैसा कि figure (a) में दिखाया गया है।
आरंभ में Figure (b) में दिखाए गए अनुसार एक दूसरे के contact में दो electrodes में low voltage का उपयोग करके एक arc भी प्राप्त किया जा सकता है। इस उद्देश्य के लिए आवश्यक low voltage को step-down transformer का उपयोग करके प्राप्त किया जा सकता है। प्रारंभ में, low voltage applied किया जाता है, जब दो electrodes एक दूसरे के contact में होते हैं। Next, जब दोनों electrodes धीरे-धीरे एक दूसरे से अलग हो जाते हैं, तो दोनों के बीच एक arc established होता है।
Arc furnaces निम्नलिखित दो प्रकार की हो सकती हैं:
(a) Direct Arc Furnance:-
इस case में, दो electrodes और charge के बीच arc इस तरह बनता है कि electric current
charge के body से होकर गुजरती है जैसा कि figure (a) में दिखाया गया है। ऐसी furnaces very high temperatures produce करती हैं।
जैसा कि figure (a) में दिखाया गया है, furnace के नीचे electric circuit का part बनता है ताकि electric charge के body से होकर गुजरे जो very low resistance प्रदान करता है। इसलिए, ऐसी furnaces में high temperatures प्राप्त करना possible है। इसके अलावा, यह
mechanically stirring के बिना एक uniform heating charge करता है।
Figure (b) में furnace के body के through से कोई current गुजरता है। इन furnaces का सबसे common application steel के उत्पादन में है क्योंकि आसानी के साथ final product की संरचना को refining करने के दौरान controlled किया जा सकता है। general use में आने वाली अधिकांश furnaces non-conducting bottom type की होती हैं, bottom conducting के
case में insulation problem के कारण।
charge के body से होकर गुजरती है जैसा कि figure (a) में दिखाया गया है। ऐसी furnaces very high temperatures produce करती हैं।
जैसा कि figure (a) में दिखाया गया है, furnace के नीचे electric circuit का part बनता है ताकि electric charge के body से होकर गुजरे जो very low resistance प्रदान करता है। इसलिए, ऐसी furnaces में high temperatures प्राप्त करना possible है। इसके अलावा, यह
mechanically stirring के बिना एक uniform heating charge करता है।
Figure (b) में furnace के body के through से कोई current गुजरता है। इन furnaces का सबसे common application steel के उत्पादन में है क्योंकि आसानी के साथ final product की संरचना को refining करने के दौरान controlled किया जा सकता है। general use में आने वाली अधिकांश furnaces non-conducting bottom type की होती हैं, bottom conducting के
case में insulation problem के कारण।
(b) Indirect Arc Furnance:-
इस case में arc का निर्माण दो electrodes के बीच होता है और इस प्रकार उत्पन्न होने वाली heat को radiation द्वारा charge पर passed किया जाता है जैसा कि figure (b) में दिखाया गया है
Figure में single-phase indirect arc furnace shows किया गया है। जो cylindrical shape में है। arc को manually रूप से or automatically रूप से moment के लिए electrodes को short circuiting करके और फिर उन्हें अलग करके निकाला जाता है। arc से heat और hot refractory lining radiation द्वारा charge की top layer पर transferred किया जाता है। charge की hot top layer से heat को conduction द्वारा charge के other parts में
transferred किया जाता है। चूंकि कोई current charge के body से नहीं गुजरता है, इसलिए electro-magnetic forces द्वारा current प्रवाहित होने वाली कोई क्रिया नहीं होती है।
इसलिए, arc की heat के लिए charge की different layers को exposing करके uniformly रूप से heat distribute करने के लिए ऐसी furnaces को लगातार rock करना पड़ता है। एक electric motor का उपयोग furnace को rocking motion प्रदान करने के लिए suitable grinders और rollers को operate करने के लिए किया जाता है। Rocking action न केवल charge को पूरी तरह से mixing provide करता है, यह refractory lining material के life को बढ़ाने के अलावा furnace की efficiency भी बढ़ाता है। चूंकि इस furnace में charge केवल radiation द्वारा
heat किया जाता है, इसका temperature direct arc furnace में उस obtainable से कम होता है। इस तरह की furnaces का उपयोग मुख्य रूप से nonferrous metals को melting के लिए किया जाता है, हालांकि इनका उपयोग iron संस्थापकों में किया जा सकता है जहां अक्सर small quantities में iron की आवश्यकता होती है।


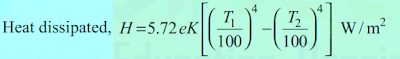














0 Comments